Significant serum K+ reduction was observed within hours with VELTASSA in real-world settings1
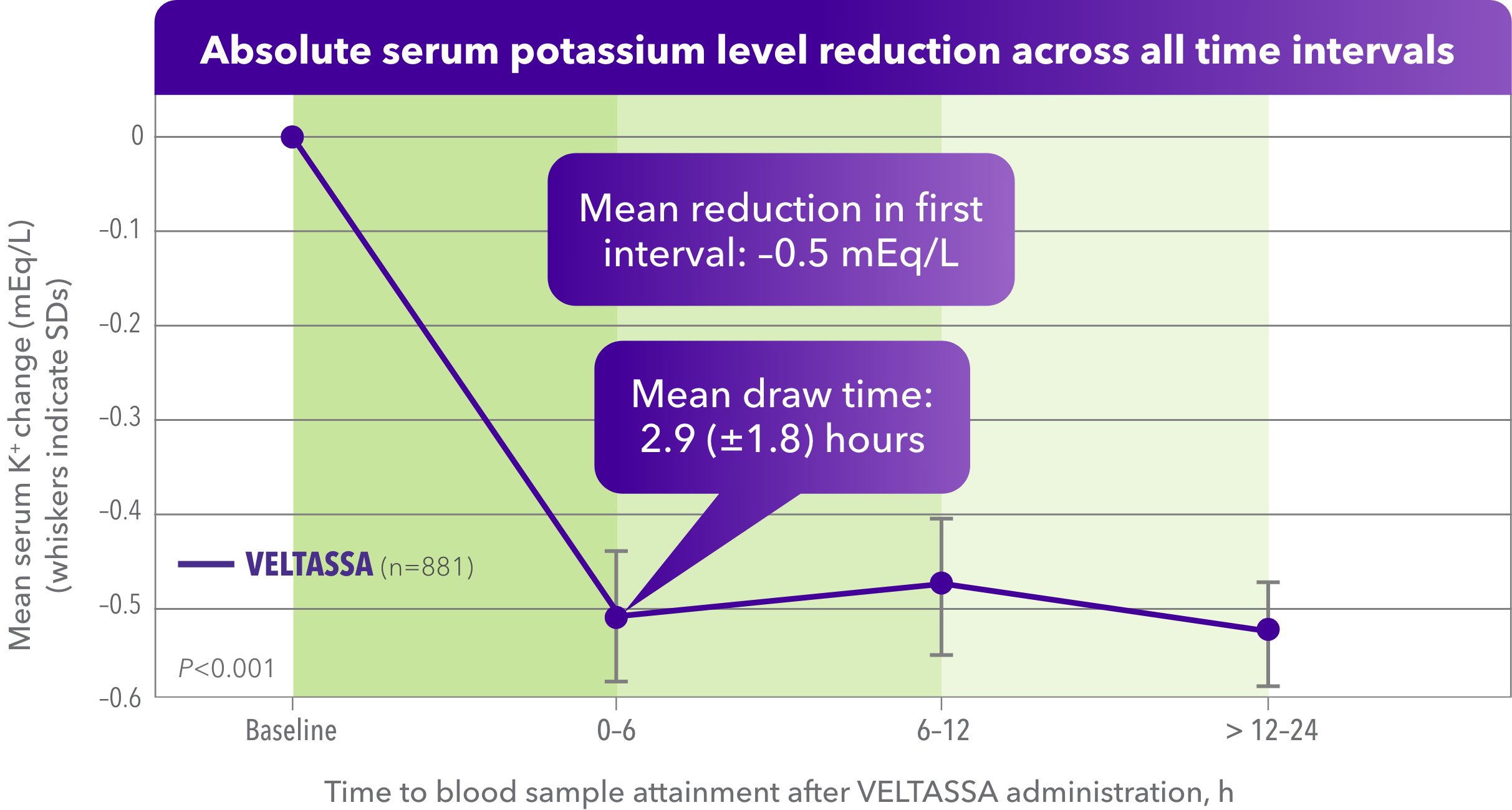
- Retrospective EHR data analysis of VELTASSA monotherapy for non–life-threatening hyperkalemia in hospitalized patients
- The lowest dose of VELTASSA, 8.4 g, was administered to 721 patients (81.8%); 82% of patients received just one dose
- Mean (SD) times of obtaining a blood sample within each prespecified interval were: 2.9 (1.8) hours; 8.9 (1.7) hours; and 17.2 (3.1) hours
Baseline K+ level, mean (SD), mEq/L: 5.60 (0.35).
Serum K+ reduction was observed within hours, rapidly and regardless of HK severity1
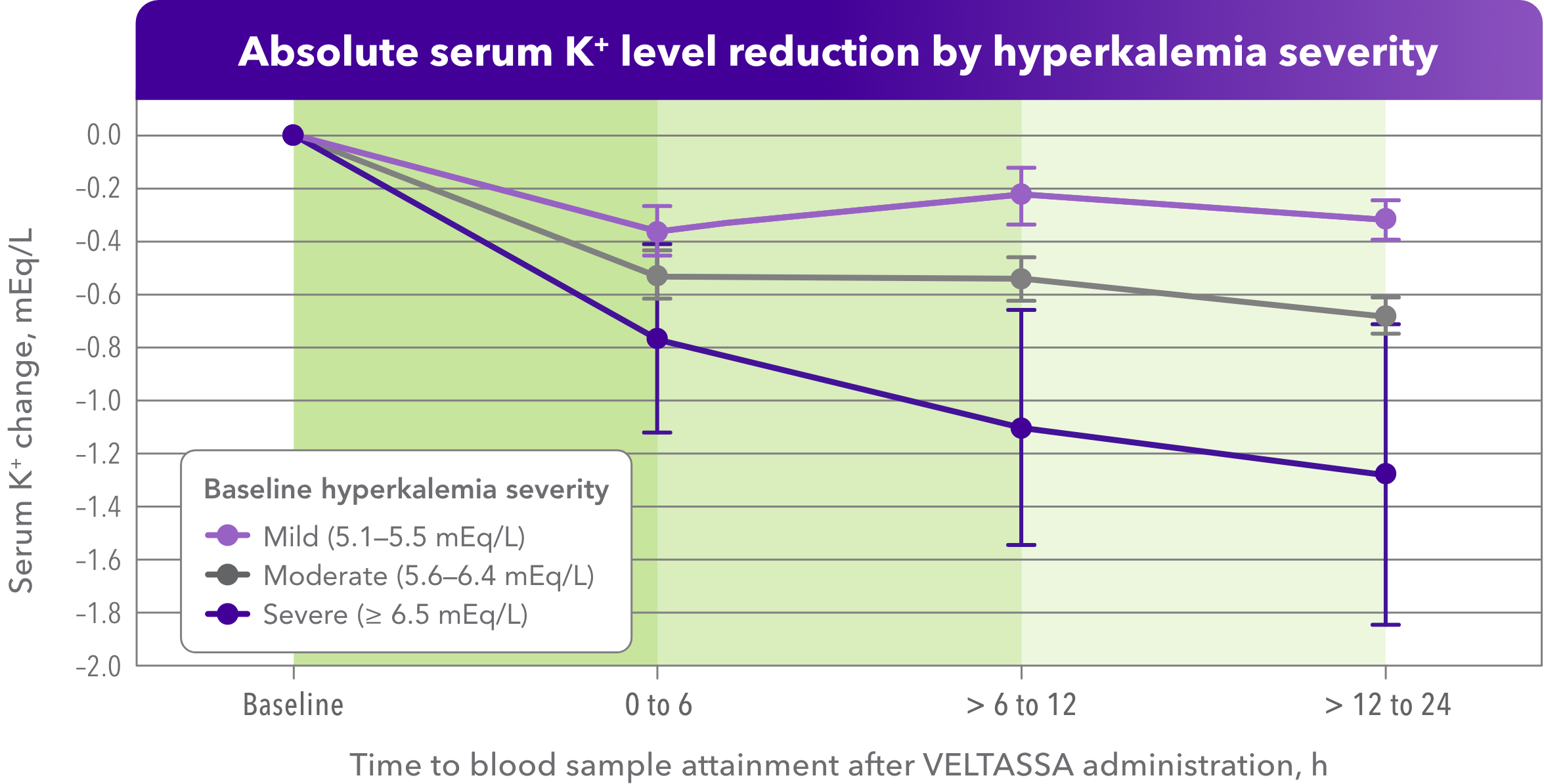
- Retrospective assessment of VELTASSA monotherapy for non-life-threatening hyperkalemia in hospitalized patients
- The association of VELTASSA with reduced serum potassium levels persisted across all baseline potassium ranges
- In 2 instances (0.2%), patients experienced a hypokalemia episode (serum K+ level, < 3.5 mEq/L), and in 68 encounters (10.0%), patients developed hypomagnesemia (serum magnesium level, < 1.7 mg/dL) after VELTASSA administration
- Both episodes of hypokalemia were mild and asymptomatic, with a serum potassium concentration between 3.2 and 3.4 mEq/L
Due to its delayed onset of action, VELTASSA should not be used as monotherapy for the emergency treatment of life-threatening hyperkalemia.
Study design
- Retrospective cohort study: Electronic health records data from January 2018 through December 2019
- Objective: Evaluate the outcomes associated with real-world VELTASSA use in 881 encounters of patients with non–life-threatening hyperkalemia in institutional settings
- Study population: Patients aged 18 years or older who received at least 1 dose of patiromer (8.4 g, 16.8 g, or 25.2 g) for the treatment of an acute non–life-threatening hyperkalemia episode, defined as a serum potassium level > 5.0 mEq/L, in any institutional setting (emergency department, inpatient unit, or intensive care unit) were included
- Primary endpoint: Mean absolute reduction in serum potassium level from baseline at 3 distinct time intervals after VELTASSA administration: 0 to 6 hours, > 6 to 12 hours, and > 12 to 24 hours
- Limitations: This study did not have a control group; therefore, whether observed reductions in potassium levels were associated with VELTASSA alone could not be determined. The absence of a protocol for treatment and monitoring of hyperkalemia required exclusion of observations from the analysis in each time interval if a laboratory blood sample was not obtained. Real-world data were retrospectively collected, are observational in nature, and are not based on controlled clinical studies
This study was supported by Vifor Pharma, Inc., as an investigator-initiated study.
VELTASSA sustained K+ control over 52 weeks
Next
