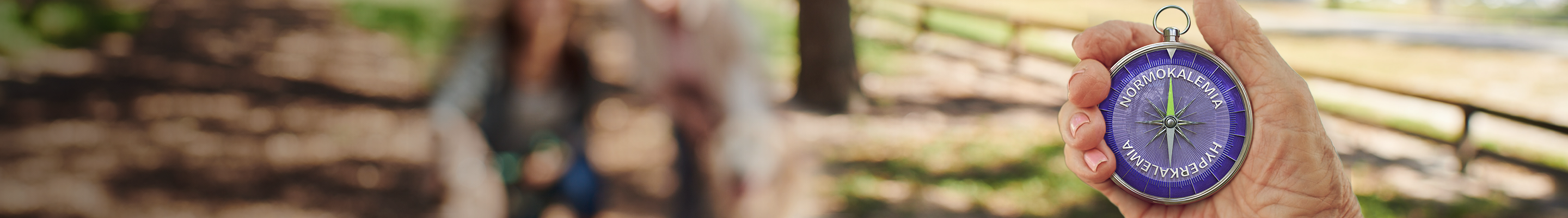
VELTASSA was shown to be safe and effective in 27 anuric adult patients on dialysis1
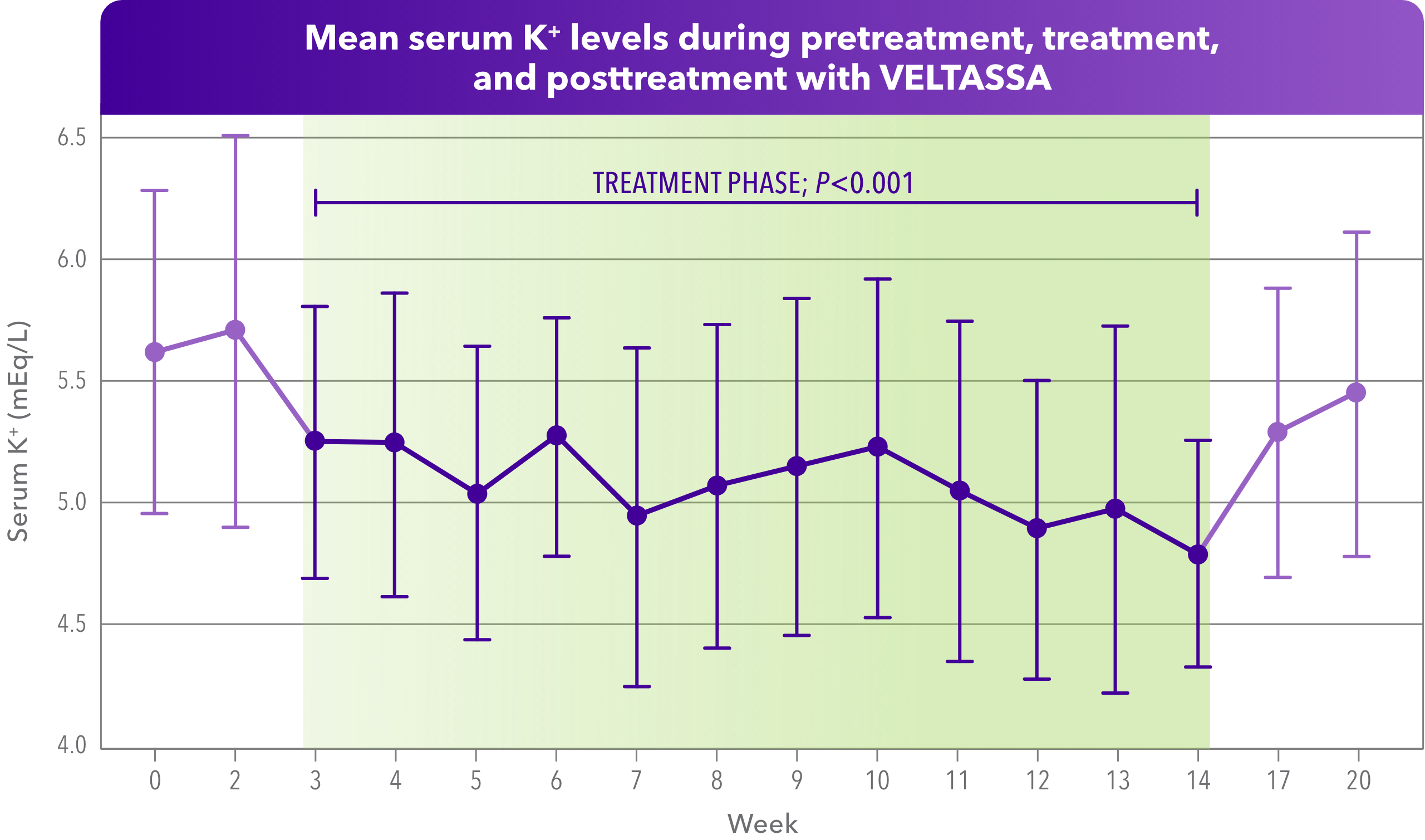
- Mean serum K+ was reduced from 5.7 mEq/L in pre-treatment to 5.1 mEq/L during treatment, then increased to 5.4 mEq/L post-treatment
Study design
A 20-week prospective study of anuric patients on hemodialysis (N=27). Serum K+ was measured during 2 consecutive weeks of no treatment, for 12 weeks of treatment with VELTASSA 16.8 g once daily, and for 6 weeks of no treatment. Primary objective was to determine the safety and efficacy of VELTASSA in reducing serum K+. Of the patients studied, the mean age was 57 years, 52% were female, 74% were African American, and 41% had diabetes.
Mean serum K+ results in a retrospective EHR analysis of > 500 adult ESRD patients on dialysis2
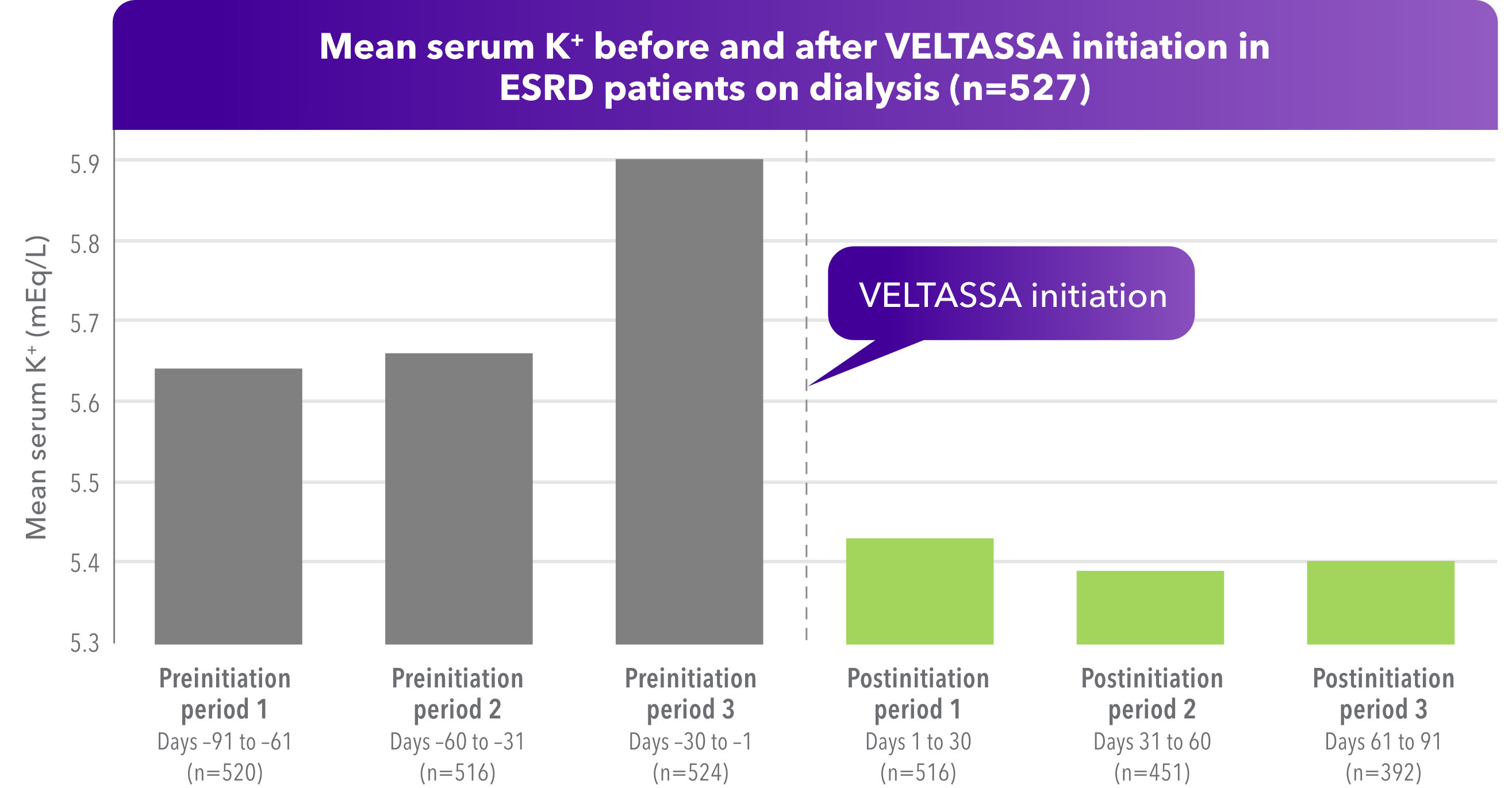
- Approximately 75% of patients had a baseline K+ of ≥ 5.5 mEq/L
- 61% (n=322) started and remained on VELTASSA 8.4 g once daily
- 75% of patients remained on VELTASSA for at least 80% of the study period
- Safety was not evaluated in this retrospective analysis
Real-world data were retrospectively collected, are observational in nature, and are not based on controlled clinical studies.
Dialysis retrospective study design
Treatment of hyperkalemia in hemodialysis patients who newly initiated VELTASSA in real-world practice
In a retrospective observational study using Electronic Health Record (EHR) data (N=527), patients (≥ 18 years) receiving hemodialysis at a large U.S. dialysis provider between December 21, 2015, and December 20, 2016, were identified. K+ values were summarized in 6 sequential 30-day periods, 3 preceding and 3 following VELTASSA initiation. Patients had at least 24 hemodialysis treatments in the 3 months prior to VELTASSA initiation. Of 527 patients studied, the mean age was 59 years, 57% were men, 70% were white/Hispanic, and 17% were black.
Significant serum K+ reduction was observed with VELTASSA in a real-world analysis of > 450 adult ESRD patients on dialysis3
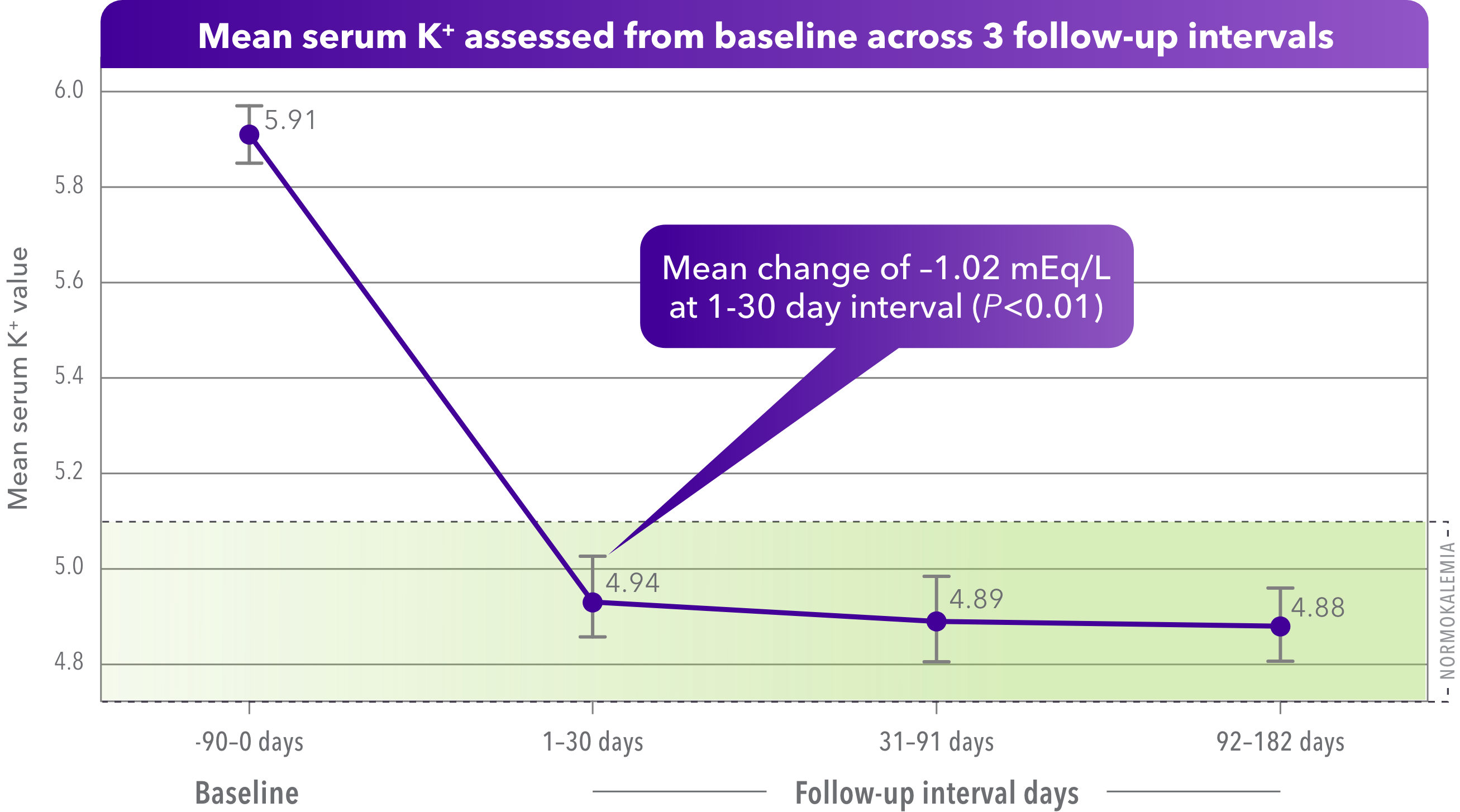
- The most common (69%; n=675) medication schedule dispensed was VELTASSA 8.4 g once daily
- 78% (n=356) of patients received only one treatment course of VELTASSA
- Safety was not evaluated in this observational study
Real-world data were retrospectively collected, are observational in nature, and are not based on controlled clinical studies.
Baseline K+ level, mean, mEq/L: 5.91 (95% CI: 5.85-5.97).
Study design
- Real-world, observational study: Electronic health record data of US veterans with ESRD (N=458) who were dispensed outpatient VELTASSA in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) from January 2016 through February 2021
- Objective: Evaluate real-world utilization of VELTASSA in an ESRD population and its corresponding association with serum K+ changes
- Study population: Patients 18 years or older with an International Classification of Diseases (ICD) diagnostic code entry for ESRD within 365 days pre-index from either an outpatient or an inpatient visit in VHA. Baseline serum K+ was ≥ 5.1 mEq/L and was determined using the laboratory event closest to the index date, within 91 days pre-index
- Primary analysis: Change between mean K+ closest to the VELTASSA index compared to mean K+ values closest to the end of the follow-up intervals
- Limitations: This study was descriptive and not designed to isolate the impact of VELTASSA on average serum K+ during the follow-up intervals. Additionally, there was no control between the timing of dialysis and K+ measurements. It is also possible that changes in serum K+ were due to a result of other influences
VELTASSA reduced serum K+ in pediatric patients
Next
