VELTASSA maintained normokalemia through 1 year1
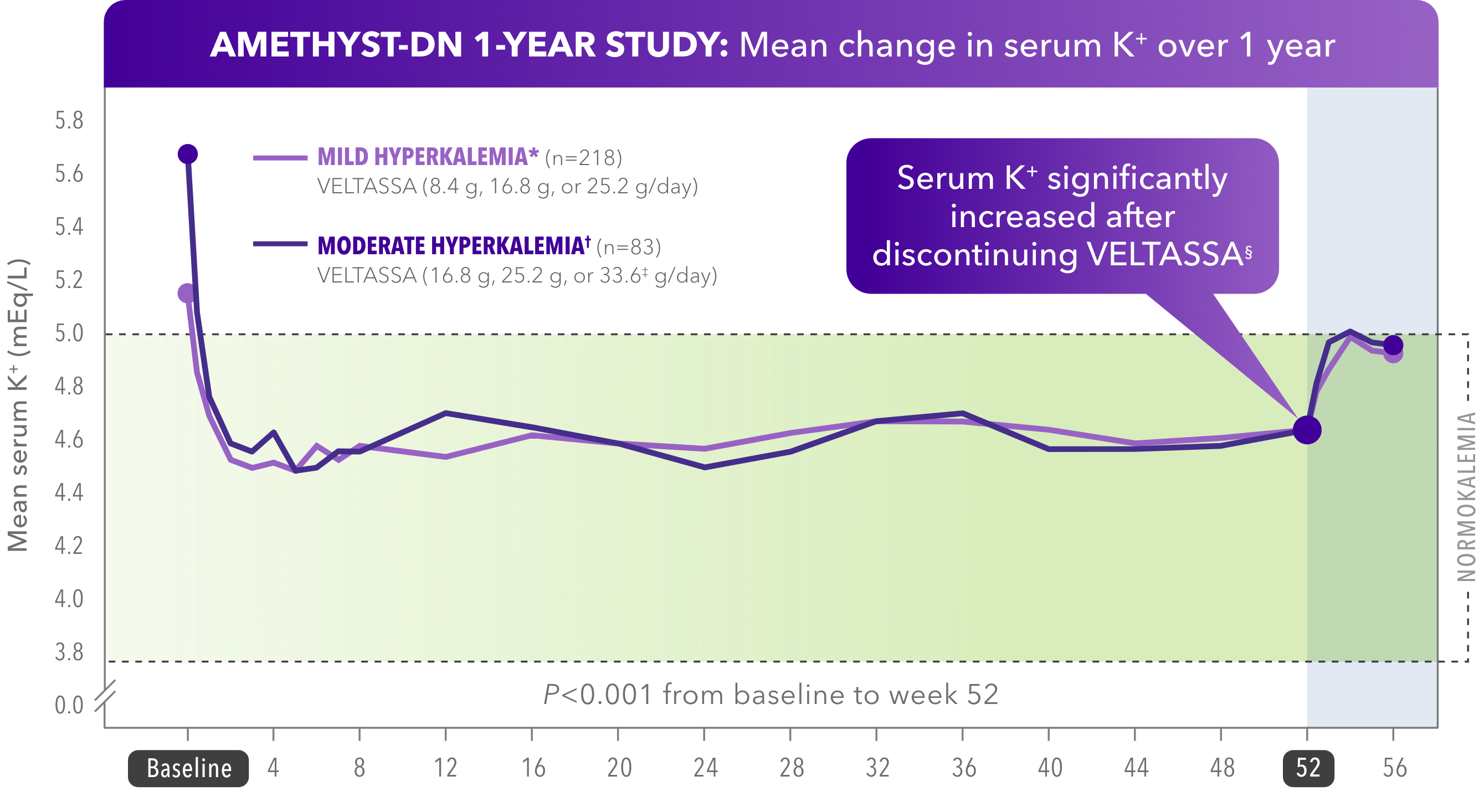
- Up to 95% of patients with hyperkalemia maintained normokalemia
- 100% of patients were on RAAS inhibitors at baseline
Normokalemia was defined as serum K+ within the target range of 3.8 to 5.0 mEq/L.
*Baseline serum K+ = > 5.0 to 5.5 mEq/L.
†Baseline serum K+ = > 5.5 to < 6.0 mEq/L.
‡Dose studied, but not commercially available.
§Significant (P<0.001) increases in least squares mean serum K+ levels were seen by day 3 post-treatment.
Study design
A phase 2, 52-week, multicenter, open-label, dose-ranging, randomized clinical trial in patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes mellitus taking RAAS inhibitors, consisting of an 8-week initiation phase and a 44-week maintenance phase. The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean change in serum K+ level from baseline to week 4 or prior to the initiation of dose titration.
VELTASSA was studied in patients like yours who are vulnerable to hyperkalemia1-5

VELTASSA data on dialysis
Next
