VELTASSA significantly lowered serum K+1
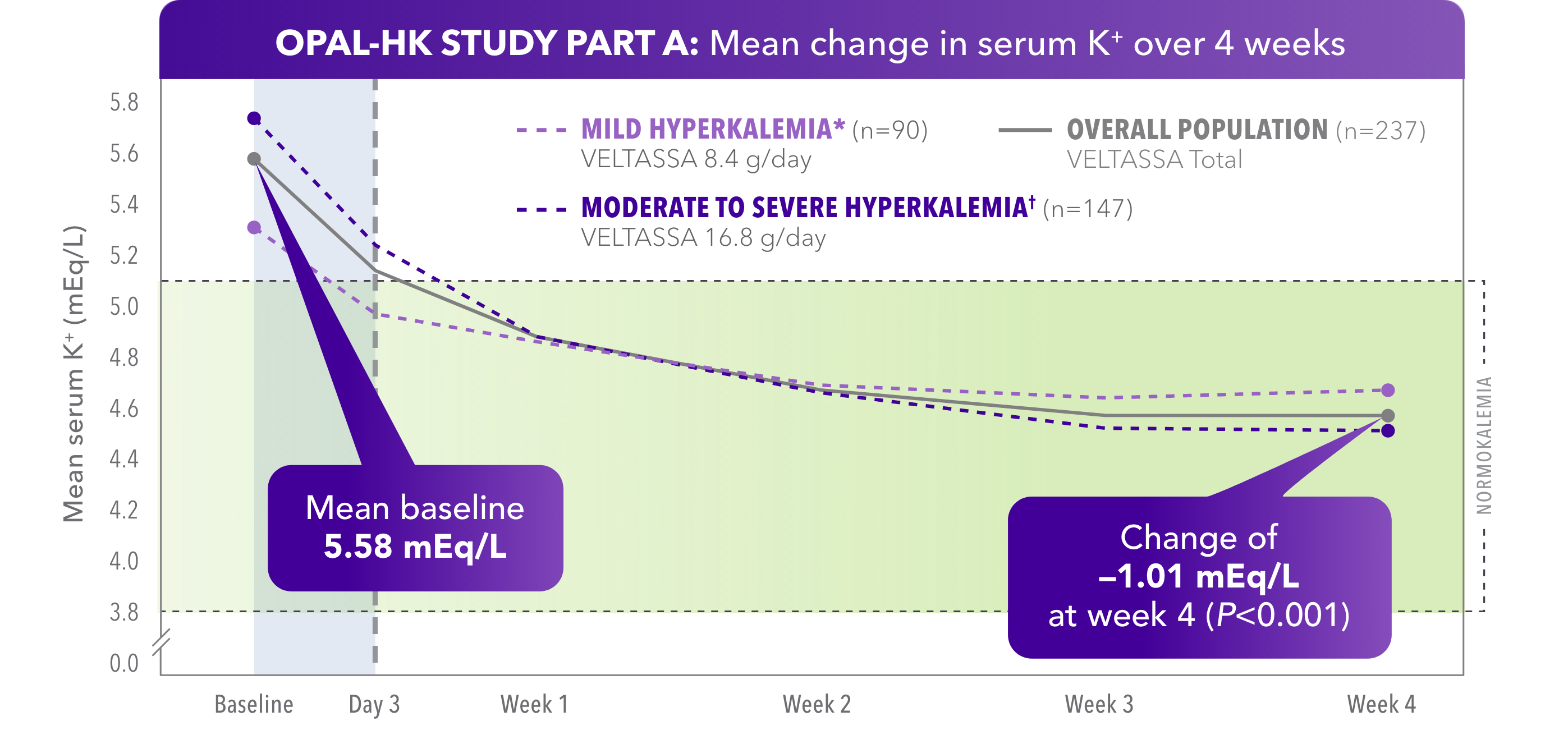
- Mean baseline of 5.74 mEq/L in moderate to severe hyperkalemia population with mean change of -1.23 mEq/L at week 4 (P<0.001)
- All patients were receiving a stable dose of RAAS inhibitors at baseline
In an exploratory analysis of the OPAL-HK 12-week study:
- 94% of VELTASSA patients remained on RAAS-inhibitor therapy at week 12, vs 44% of placebo patients
Normokalemia was defined as serum K+ within the target range of 3.8 to < 5.1 mEq/L.
The mean change in patients with mild hyperkalemia from baseline (5.31 mEq/L) was -0.65 mEq/L (P<0.001).
*Baseline serum K+ = 5.1 to < 5.5 mEq/L.
†Baseline serum K+ = 5.5 to < 6.5 mEq/L.
Study design
A phase 3, 2-part, 12-week, multicenter study consisting of a 4-week, single-group, single-blind initial treatment phase and an 8-week, placebo-controlled, single-blind, randomized withdrawal phase in adult patients with CKD stage 3 or 4. Patients had serum K+ of 5.1 to < 6.5 mEq/L and were receiving a stable dose of RAAS inhibitors.
Exploratory analysis in the OPAL-HK 12-week study
Treatment of hyperkalemia in patients with CKD taking RAAS inhibitors
The Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) defined exploratory efficacy outcomes that measured the proportion of patients receiving any dose of RAAS inhibitors at week 8 in Part B of the study.
VELTASSA was studied in patients like yours who are vulnerable to hyperkalemia1-5

VELTASSA worked within hours for low-K+ diet–resistant HK patients
Next

