Knowing what foods are high in potassium is important.
If your kidneys are having trouble removing potassium from your body, eating foods that are high in potassium may make your condition worse. Here’s a helpful list of some of the high-potassium foods you should limit or avoid. Remember: Always ask your healthcare provider for guidance on which foods are best for you.
High-potassium foods
Here are some foods to avoid or limit in your diet:
Fruits
Avocados, bananas, oranges, nectarines, kiwifruit, mangos, papayas, prunes, pomegranates
Vegetables
Brussels sprouts, potatoes, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, tomatoes, spinach, beans and legumes, vegetable juices
Other
Salt substitute, milk, granola, nuts and seeds, peanut butter
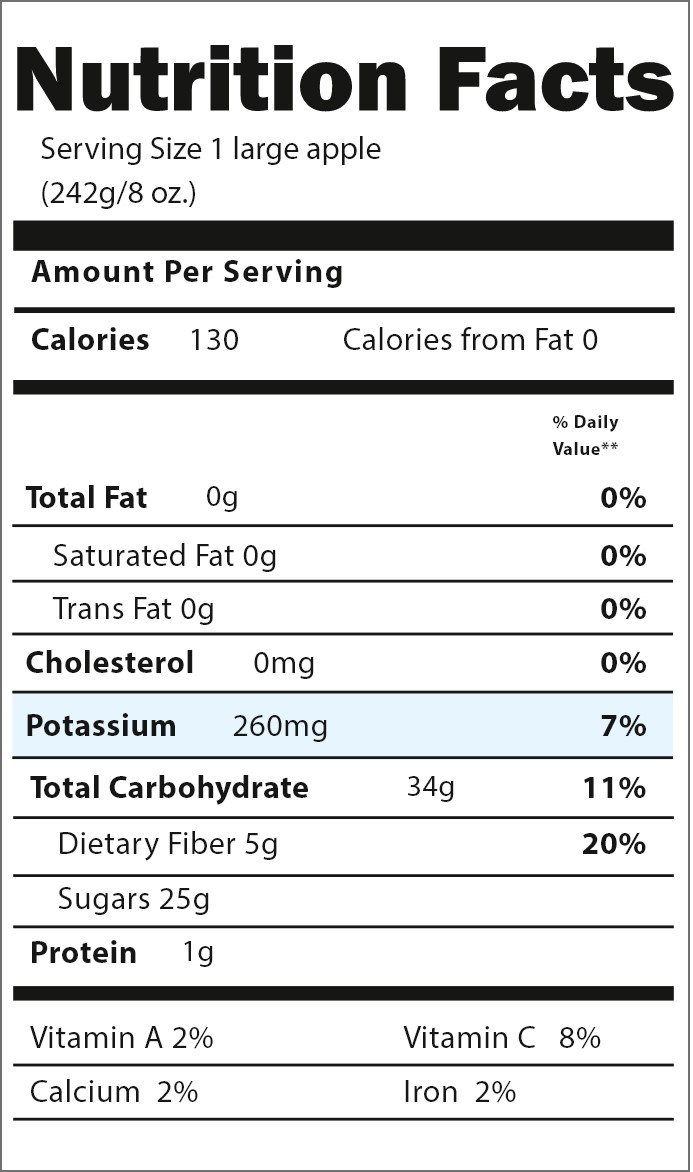
How much potassium is in your food? Read the label.
Find out how much potassium is in the foods you buy by reading the Nutrition Facts on the label. Potassium, like other nutrients, is listed as a percentage of the Recommended Daily Allowance (or RDA). The RDA is for people who do not have health conditions like high potassium.
Did you know?
Healthy adults should have 3,500 mg of potassium each day. Your needs may be different if you follow a low-potassium diet. Be sure to ask your doctor how much potassium you should have each day.
